
Your leaky ductwork may be hiking up your energy bills. We explore the cost of checking air ducts for leaks, which may be worth it for your home.
You can easily have lower energy bills and cleaner air


Air duct insulation improves your HVAC system’s energy efficiency and performance.
A higher R-value means better insulation performance
Air duct insulation requirements vary by state and local ordinances.
Insulation is often required in cold climates and when ducts are in unconditioned spaces.
Air duct insulation is a crucial aspect of maintaining a comfortable indoor environment and an energy-efficient home. But when is insulation required on air ducts, and what are the benefits? Whether you’ve recently purchased your home and discovered uninsulated ducts or you’re just noticing some problems in your HVAC system, understanding air duct insulation is important. Let’s discuss whether insulating your air ducts should be your next home improvement project.
Duct insulation refers to the practice of adding insulation material to the walls of air ducts. This insulation acts as a barrier, preventing heat transfer between the ducts and the surrounding environment. In simpler terms, it keeps your conditioned air at the desired temperature as it travels through the ductwork. This ensures that the air reaches its destination without losing its thermal properties.
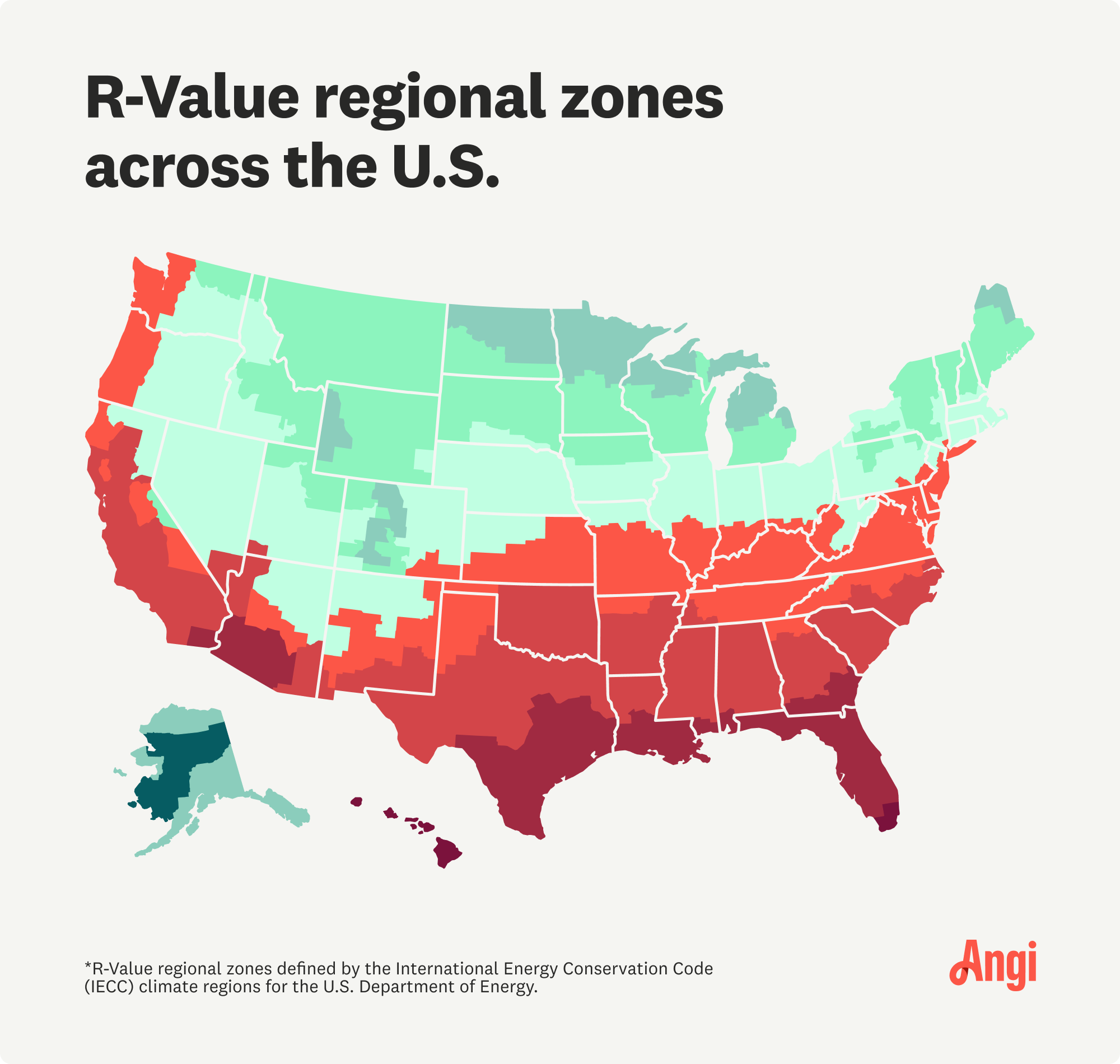
The R-value is a critical factor when it comes to choosing the right insulation for your air ducts. This term refers to the measurement of a material's thermal resistance and indicates how effective it is at inhibiting heat flow.
So, what is R-value in the context of duct insulation? Basically, a higher R-value means better insulation performance. Choosing the right R-value ensures that your ducts can maintain the desired temperature efficiently.
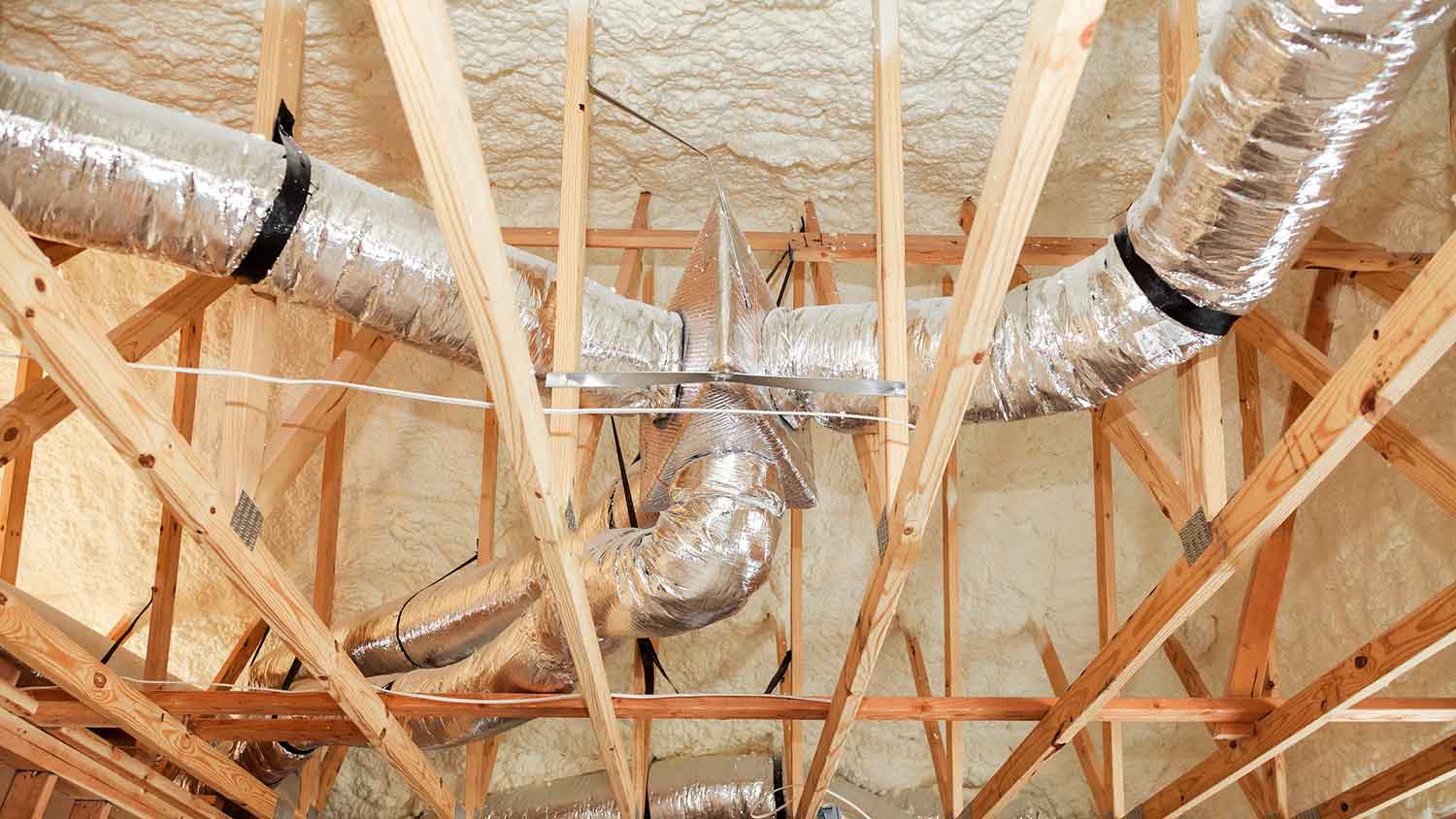

If you’re wondering whether it’s necessary to insulate your air ducts, you need to understand all the amazing benefits that come along with this project. While there is certainly an upfront cost of air duct insulation, these benefits mean the insulation will pay for itself in time.
One of the primary advantages of insulating your air ducts is improved energy efficiency. Insulated ducts minimize heat loss or gain during the distribution of conditioned air, which can lead to significant energy savings over time.
Insulation also helps in reducing moisture buildup within the ducts. Moisture can lead to mold growth, which not only affects indoor air quality but also poses health risks. Proper insulation acts as a moisture barrier, preventing mold from growing inside your ducts.
Similar to inviting mold growth, uninsulated ducts can also be an entry point for insects and rodents. Pest infestation in your air ducts can cause a whole host of problems, including damage to your HVAC system as well as health hazards from waste and carcasses.
Insulation adds an extra layer of protection, making it more challenging for unwanted visitors to find their way into your ductwork.
HVAC systems naturally generate some noise, which can be disruptive to your home. When you insulate your ducts, it can help reduce noise transmission from the heating and cooling system, creating a quieter and more peaceful indoor environment.
Uninsulated air ducts can contribute to poor indoor air quality by allowing dust, contaminants, and moisture to enter the ductwork. Without insulation, these elements can accumulate and circulate throughout the living spaces, potentially leading to health issues, allergen exposure, and less comfortable living space.
Duct insulation can contribute to better indoor air quality by preventing these irritants and pollutants from entering the ducts and circulating throughout your living spaces.
When air ducts are uninsulated, they can strain HVAC systems as they fail to maintain the desired indoor temperature efficiently. In extreme temperatures, these ducts allow heat loss or gain, causing the HVAC system to work harder and consume more energy. This increased workload can lead to premature wear and tear and reduced overall system performance.
Efficiently insulated ducts, on the other hand, ensure that your HVAC system doesn't have to work as hard to maintain the desired temperature, extending its lifespan and reducing HVAC maintenance costs.
There are certainly a host of benefits when it comes to insulating your air ducts, but there are some situations in which insulation is required by law. However, air duct insulation requirements can vary significantly from one state or local area to another.
To determine the specific requirements in your region, you should contact your local building codes or energy efficiency programs. You can also consult with local HVAC professionals or visit government websites for information on insulation standards and recommendations tailored to your location.
In general, there are a few situations in which insulation is commonly required on air ducts.
In regions with very cold winters or high humidity, air duct insulation becomes crucial. It helps maintain the desired temperature of conditioned air and prevents condensation on air vents, which can lead to mold growth and other problems, as we mentioned earlier.
When air ducts are located in unconditioned spaces—such as attics or crawl spaces—they often require insulation to protect them from extreme temperature fluctuations.
There are a lot of different types of air duct materials and some are more energy efficient than others. For example, sheet metal air ducts are among the most energy-efficient air ducts, while flexible air ducts tend to lose more energy due to frequent tears and damage.
If your ducts are made of materials with low energy efficiency, like thin flexible ducts, insulation is essential to compensate for their inadequacy.
Leaking or damaged ducts should be repaired or replaced as soon as possible since they can result in energy waste, pest infiltration, and decreased system performance. Insulating them can help mitigate these issues temporarily.
While older ductwork doesn’t necessarily need to be replaced immediately, it may not have been designed with energy efficiency in mind. Insulating older ducts can significantly improve the overall performance of your HVAC system.
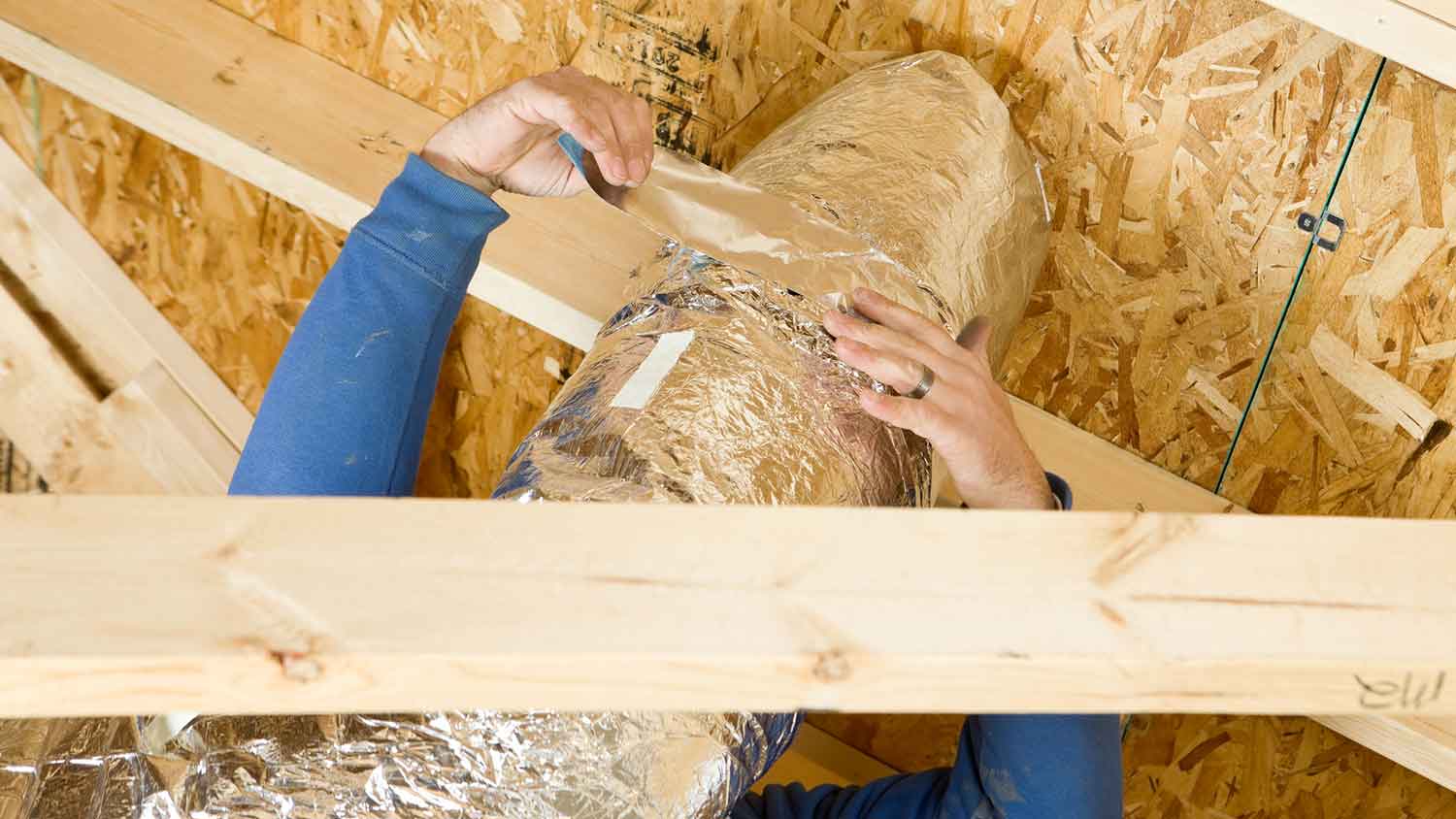

Duct insulation costs $1,000 to $2,700, but most homeowners spend around $2,500. Costs vary based on the material, with fiberglass blankets costing around $1 to $4 per square foot compared to spray foam costing $8 to $13 per square foot. As with all insulation projects, expect to pay more for thicker insulation with a higher R-value.
While it's possible to take on this DIY project if you know how to insulate ductwork, it's often recommended to hire the pros. They have the expertise to ensure that the insulation is applied correctly and that the job is done efficiently and safely.
If you’re not confident in your ability to insulate your air ducts in a way that will ensure a safe, efficient, and damage-free installation, enlist the help of a local duct installer for this task.
From average costs to expert advice, get all the answers you need to get your job done.

Your leaky ductwork may be hiking up your energy bills. We explore the cost of checking air ducts for leaks, which may be worth it for your home.

If your air conditioning unit isn’t functioning properly, you might need an AC recharge. Our guide will detail what a typical AC recharge cost looks like.

What you’ll pay in Columbus, OH, for furnace repairs depends on many factors. Here’s a breakdown of what can go wrong and the cost to fix those issues.

Tackling unwanted odors from indoor plants can be tricky. Learn how to use a carbon filter in your duct fan to improve air quality.

Having dirty evaporator and condenser coils works your HVAC system harder than it needs to. Here’s how to clean your air conditioner coils like a pro.

Not sure which kind of thermostat is best for your home? Here’s an overview of three types of thermostats so that you can choose the right one for you.