
A blower door test can identify air leaks in your home and help boost energy efficiency. Use this blower door test cost guide to see what your test will total.
With this system, the heat’s underneath your feet


Radiant heating is an energy-efficient way of heating your home.
There are two main types of radiant heating systems: hydronic and electric.
These systems use hot water or electrical coils to create and transfer heat into your home.
They’re often installed underneath floors but can also go behind walls or above ceilings.
You can use radiant heating to warm individual rooms or your whole house.
Can’t stand your bare feet touching the cold floor on a chilly winter morning? A radiant heating system could be the solution you’ve been searching for. This efficient type of home heating distributes heat quickly and evenly. Plus, it doesn’t use ducts, so it’s allergy-friendly. Read on to learn more about radiant heating systems, including the pros, cons, and types.
Radiant heating is a type of home heating system. It relies on radiant heat—or the transfer of heat from a hot surface to a cooler one—to warm up your living space. For example, in the case of radiant floor heating, there are electric wires or hot water tubes underneath the flooring that produce and transfer heat to the flooring above. You can also use radiant heating in walls and ceilings (but it’s most often found under floors to warm up your tootsies on those cold mornings).
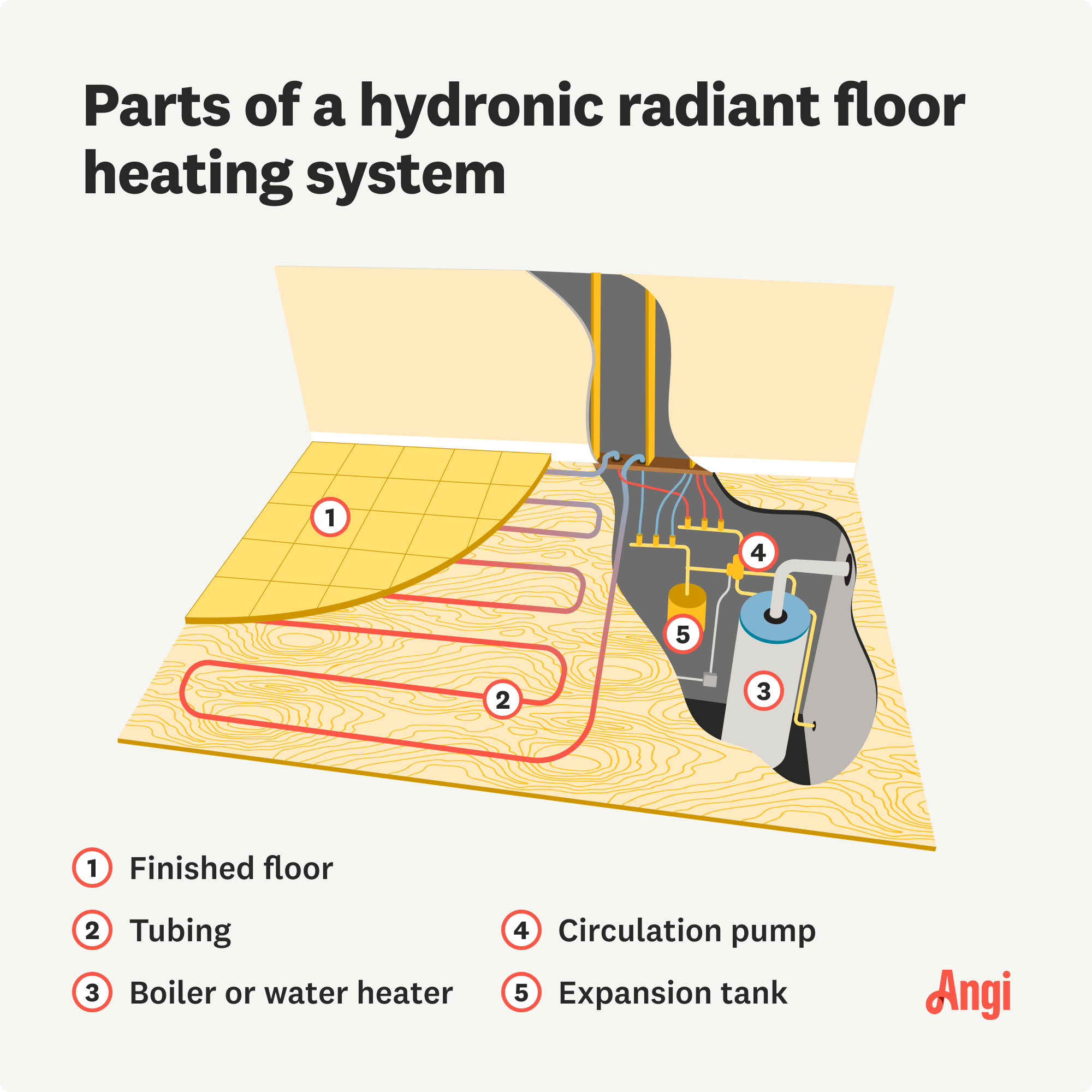
Each type of radiant heating system functions differently, but the outcome is the same.
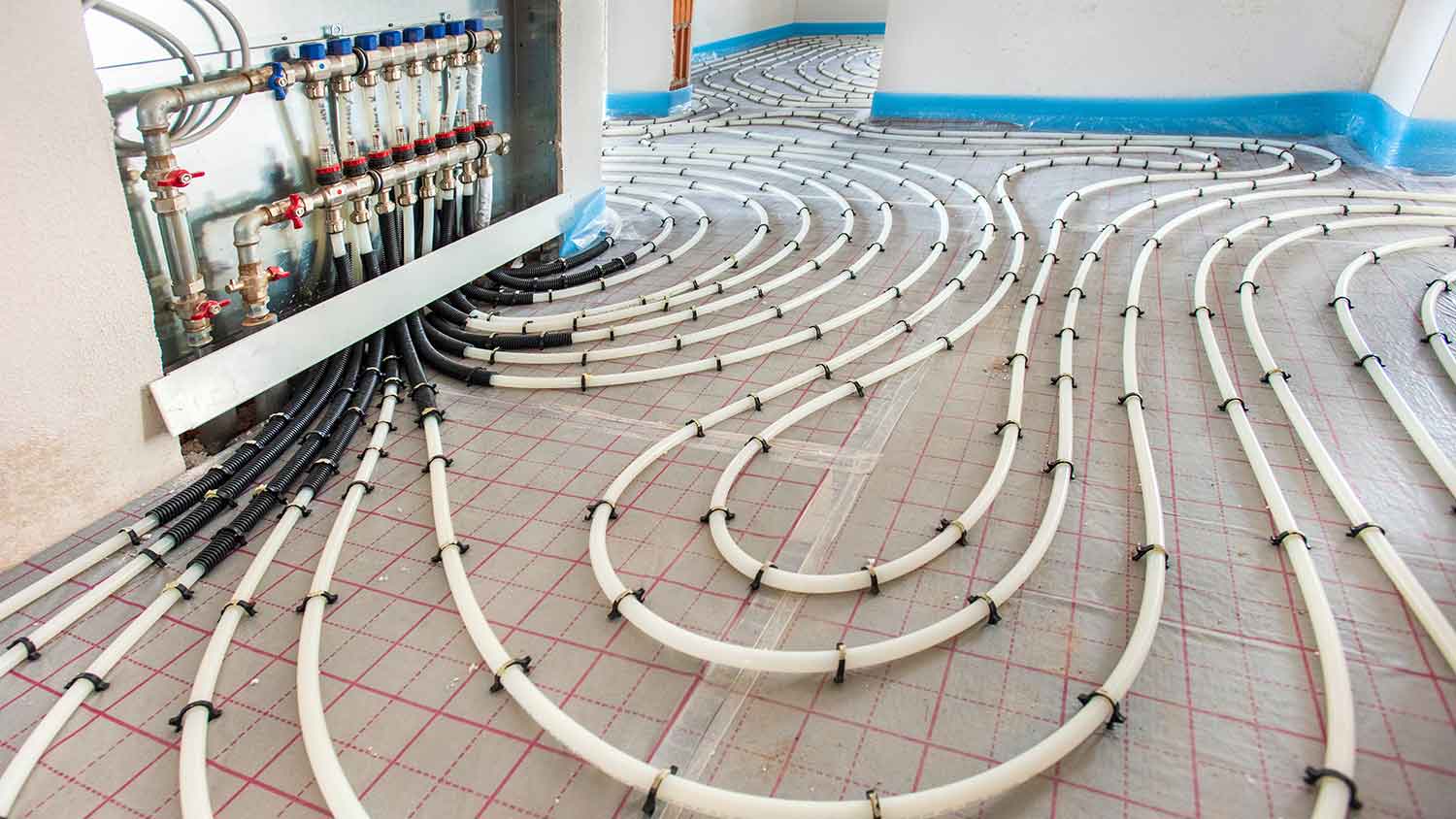
In a radiant floor heating system, you’ll find a series of pipes, tubes, or wires that run beneath the floor. They can be configured in several ways, including being fastened to the subfloor, connected to a panel, or embedded into concrete. This tubing system creates heat (either through electricity, hot water, or heated air), which rises, warms up the floors, and transfers into the rest of the room.
The process works similarly in walls and ceilings. However, in these installations, the radiant heating tubes are attached to panels. For wall heating, the panels are installed along the lower portion of the wall.

There are two main kinds of radiant heating systems: hydronic and electric. However, those aren’t the only options.
Hydronic heating systems are efficient and suitable for whole-house heating. They have a water heater or boiler, which heats up water and sends it through a series of tubes to release heat into your home. It’s possible to add hydronic radiant heating to an existing house, but it’s simpler to install this type of radiant heating system while building a home.
Electric systems use electric wires or coils to generate heat. On the plus side, they heat up quickly and are easier to install than hydronic systems. However, electric systems are best used in smaller areas or as a supplemental heating source rather than warming up an entire home.
Aside from hydronic and electric systems, there are a few other radiant heating systems with distinct heat sources available for home heating. These include:
Geothermal: Geothermal systems use thermal energy and heat pumps to disperse natural heat under your floors.
Solar: These eco-friendly systems use energy from the sun to heat your home.
Propane: Propane-powered systems are the most affordable radiant heating option.
Air-heated: These radiant heating systems send hot air through ducts underneath your flooring. As the air rises, it heats up your room. However, these systems aren’t as cost-effective as others, so they aren’t installed in homes very often.
While each type of radiant heat system has its own pros and cons, there are a few consistent benefits and drawbacks to this type of home heating system.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Energy efficient | Some types are expensive to install |
| Distributes heat evenly and quickly | Retrofitting a home with radiant heating can be costly and complicated |
| Quieter than many other heating methods | May increase a floor’s height |
| Doesn’t circulate dust, hair, or allergens | Hydronic systems may leak or cause water damage |
On average, installing radiant floor heating costs between $1,600 and $6,600, but prices depend on the type of radiant heating system, the size of the area, and other factors. Here’s how much a local HVAC company might charge to install the most common types of radiant floor heating:
| Radiant Floor Type | Average Installation Cost |
|---|---|
| Hydronic | $19,000–$48,000 |
| Electric | $19,000–$36,000 |
| Geothermal | $9,500–$27,000 |
| Solar | $8,000–$19,500 |
| Propane | $2,400–$2,900 |
From average costs to expert advice, get all the answers you need to get your job done.

A blower door test can identify air leaks in your home and help boost energy efficiency. Use this blower door test cost guide to see what your test will total.

HVAC replacement costs depend on a lot of factors, like unit type, size, and labor. See what you can expect to pay for HVAC replacement here.

Find out the average humidifier repair cost, what impacts pricing, and how to save. Get expert tips to budget for your humidifier repair.

Tackling unwanted odors from indoor plants can be tricky. Learn how to use a carbon filter in your duct fan to improve air quality.

Learn about the different types of electric furnaces to decide why you would use one and which option is best for replacing your home heating system.

You’ll need to get creative if you want to run your portable AC in a windowless room. Here’s how to vent a portable air conditioner without a window.