
Need to know what sewer line replacement costs in New York, NY? This guide will help you prepare to budget for sewer line replacement done by local contractors.
Drain the murky mysteries of septic systems with this guide


A septic system uses pipes, a tank, filters, and soil to treat household wastewater.
Septic tanks need to be pumped by a professional every three to five years.
A septic system lasts 20 to 40 years on average.
It costs $3,500 to $11,750 to install a new septic system.
Repairs cost $630 to $3,000 on average.
When you rinse your hair in the shower, wash off a dinner plate in the kitchen sink, or flush a toilet, you may not give much thought to where all that wastewater goes. But if you live on a property with a septic system, it’s actually important for you to understand the inner workings of this essential wastewater management system. From the pipes in your home to the drain field in your backyard, here’s how a septic system works.
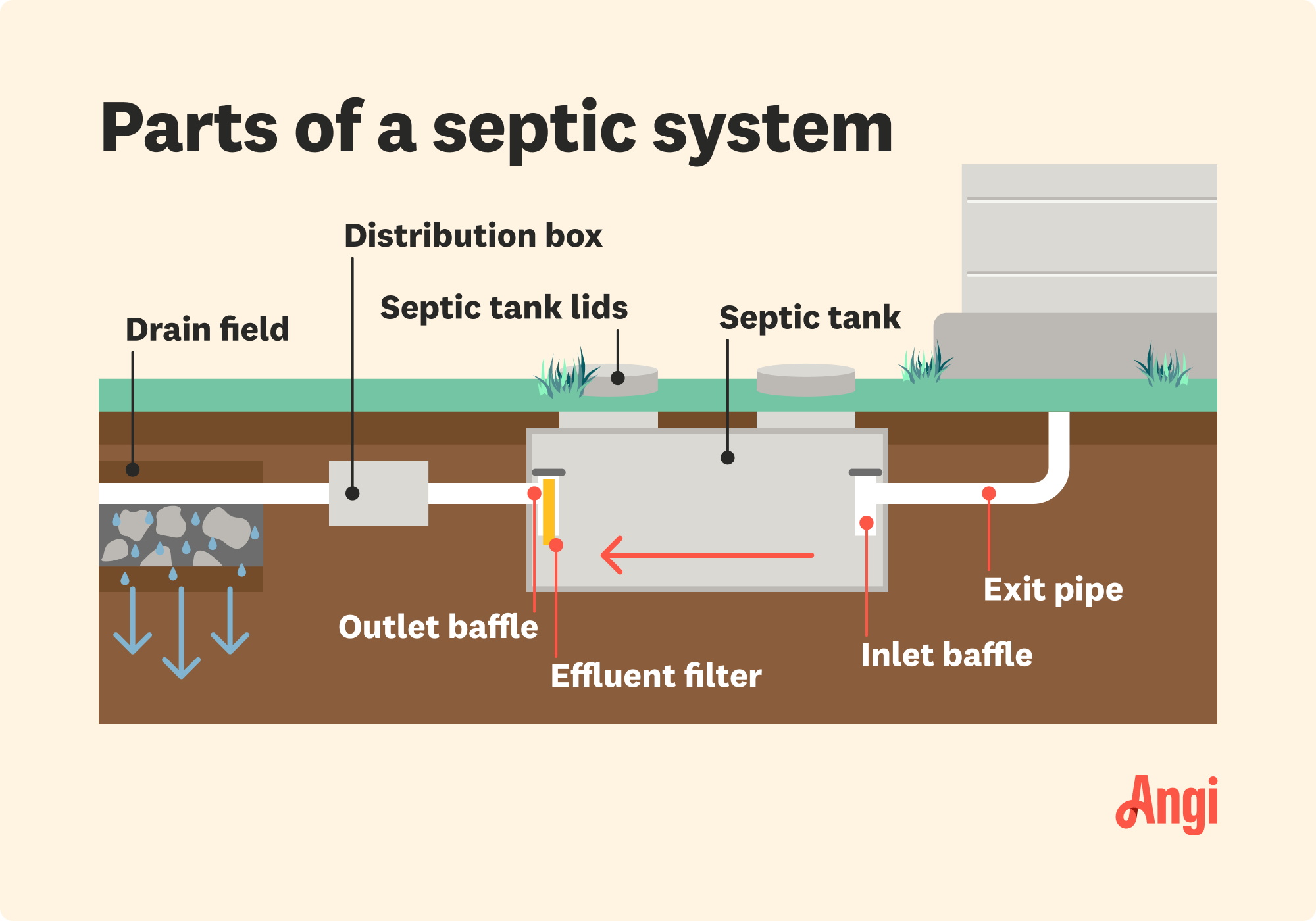
To better understand how a septic system works, it’s helpful to know the different parts of the septic system and how they all connect to carry wastewater away from your home, ultimately returning it as treated water into the soil.
The exit pipe is where the wastewater, which comes through your home’s plumbing from drains in appliances, sinks, toilets, and bathtubs, will move out of the home and toward the septic system.
The baffles are the inlet and outlet pipes to the septic tank. Wastewater travels from the exit pipe of the home to the inlet baffle of the septic tank. When the water is partially treated, it’s ready to later move to the outlet baffle at the other end of the septic tank.
The septic tank is a large, buried container made from plastic, fiberglass, or concrete. This tank is designed to hold wastewater, including black water from toilets and greywater from sinks, showers, and appliances.
The effluent filter is located near the outlet baffle of the septic tank. This filter helps remove contaminants like oils, fats, and grease from wastewater before it continues through the septic system.
The distribution box, or D-box, connects to various pipes through a drain field, where wastewater goes for final treatment and slowly disperses into the ground. The distribution box helps evenly distribute wastewater to different pipes for proper treatment and dispersal without overwhelming one pipe.
The drain field is where the partially treated wastewater, or effluent, from the septic tank flows for final dispersal into the soil. The field is made up of several leach lines or septic lateral lines.
Leach lines are positioned along the length of the drain field. They have perforations to let effluent drain slowly into the soil, where bacteria help finish treating the wastewater before it returns back to the groundwater and local ecosystem.
So, how does a septic system work, anyway? There are several steps to the process, and it all starts with water inside your home.
First, any wastewater from around the home—such as from toilets, sink drains, tubs, showers, or appliances—will drain away into the pipes of the home and through to the sewer line of the home. This wastewater then travels to the exit pipe to take it out of the home and toward the septic system.
Next, the wastewater travels into the inlet baffle and goes into the septic tank. In this tank, the solids in the wastewater separate and sink to the bottom of the tank while the water sits just above it. Any remaining liquid contaminants, like oil or grease, float to the top. These floating contaminants are known as scum, and the solids that sink to the bottom of the tank are known as sludge. Bacteria that live in the tank help break down some of the waste.
The water continues flowing down the line while the sludge and scum remain in the tank, and the water is treated at an effluent filter before exiting the septic tank as treated water through the outlet baffle.
Finally, the effluent travels to one or more distribution boxes and to the septic lateral lines. The effluent slowly disperses out into the soil, where it is further treated by aerobic bacteria. The water eventually reaches the groundwater after being fully treated by the bacteria.
There are other types of septic systems than this conventional setup, though, and they work in slightly different ways. For example, aerobic treatment units add oxygen to the septic tank to feed aerobic bacteria, an ideal setup for properties with soil that isn’t well-suited to treating effluent. Another example is recirculating sand filter septic systems, which use pumps to move wastewater to sand filters for treatment.

Maintaining your septic system is important to prevent clogs and leaks that can cause expensive damage to your septic system and home’s plumbing. Here are some ways you can maintain your septic system:
Pump the septic tank: Pump the septic tank often, about every three to five years, to remove sludge buildup.
Schedule inspections: Hire a pro to perform annual inspections to catch any minor repairs before they become bigger problems.
Replace the biomat: The biomat is a layer of bacteria and other biomaterials under the soil in the drain field. Over time, it can build up and cause clogs. Pumping the tank helps prevent biomat problems, but older systems over 25 years may need biomat replacement.
Avoid flushing or draining certain items: Too many fats and oils, food waste, sanitary items, and even certain chemicals and skin care products can clog the septic tank.
Fabric softener can be tough on your washing machine and tough on your septic system. If you use fabric softener, put a small cup of vinegar in with your clothes instead of softener every couple of washes. Vinegar can soften your clothes and break down the fabric softener residue.
The life span of a septic system is 20 to 40 years, depending on factors like what material the septic tank is made of and how often you schedule professional sludge pumping. Concrete septic tanks tend to last the longest, up to 100 years, while plastic has a shorter life span. By hiring a local septic tank company to pump the tank every three to five years and perform annual inspections, you’ll get more life out of the septic system.

Whether you need to install a new septic system entirely or you’re just budgeting for the next inspection, there are several costs to consider when it comes to owning a septic system. Some costs you can expect for septic systems may include:
Septic system installation cost: $3,500–$11,750
Septic system inspection cost: $200–$900
Septic tank pumping cost: $250–$1,250
Septic system repair cost: $630–$3,000
From average costs to expert advice, get all the answers you need to get your job done.

Need to know what sewer line replacement costs in New York, NY? This guide will help you prepare to budget for sewer line replacement done by local contractors.

Need to know what sewer line replacement costs in Chicago, IL? This guide will help you prepare to budget for sewer line replacement done by local contractors.

Sewer cleanout costs depend on the type of cleanout and how long the line will be. Click here to start planning your budget for this project.

Need to know what sewer line replacement costs in Houston, TX? This guide will help you prepare to budget for sewer line replacement done by local contractors.

Cleaning out clogged or dirty septic field lines is a quick job for a seasoned pro. Learn what makes up the total cost to clean septic field lines

Need to know what sewer line replacement costs in Denver, CO? This guide will help you prepare to budget for sewer line replacement done by local contractors.