
Discover the average hot tub maintenance cost, what impacts pricing, and how to save money. Get expert tips to keep your hot tub running smoothly all year.
Find out how a heater puts the “hot” in hot tub


Most hot tubs use an electrically resistant coil to heat water.
The safe temperature range for a hot tub is 93°F to 100°F.
Hot tubs take an average of four to eight hours to heat up.
You can replace a hot tub heater if need be.
A hot tub is a tried-and-true tool for relaxation. Like any tool, however, you should understand how it works so you can properly address any potential issues that may arise. Because the heater is the most important part of any hot tub, this article will go in-depth on how it works.
The hot tub itself consists of two main parts: the shell and the cabinet. The shell is the tub's exterior, while the cabinet houses the heater and other parts crucial to the hot tub’s function. Maintaining the high temperature of the water in a hot tub requires an electrical resistance heater, a thermostat, and a control panel.
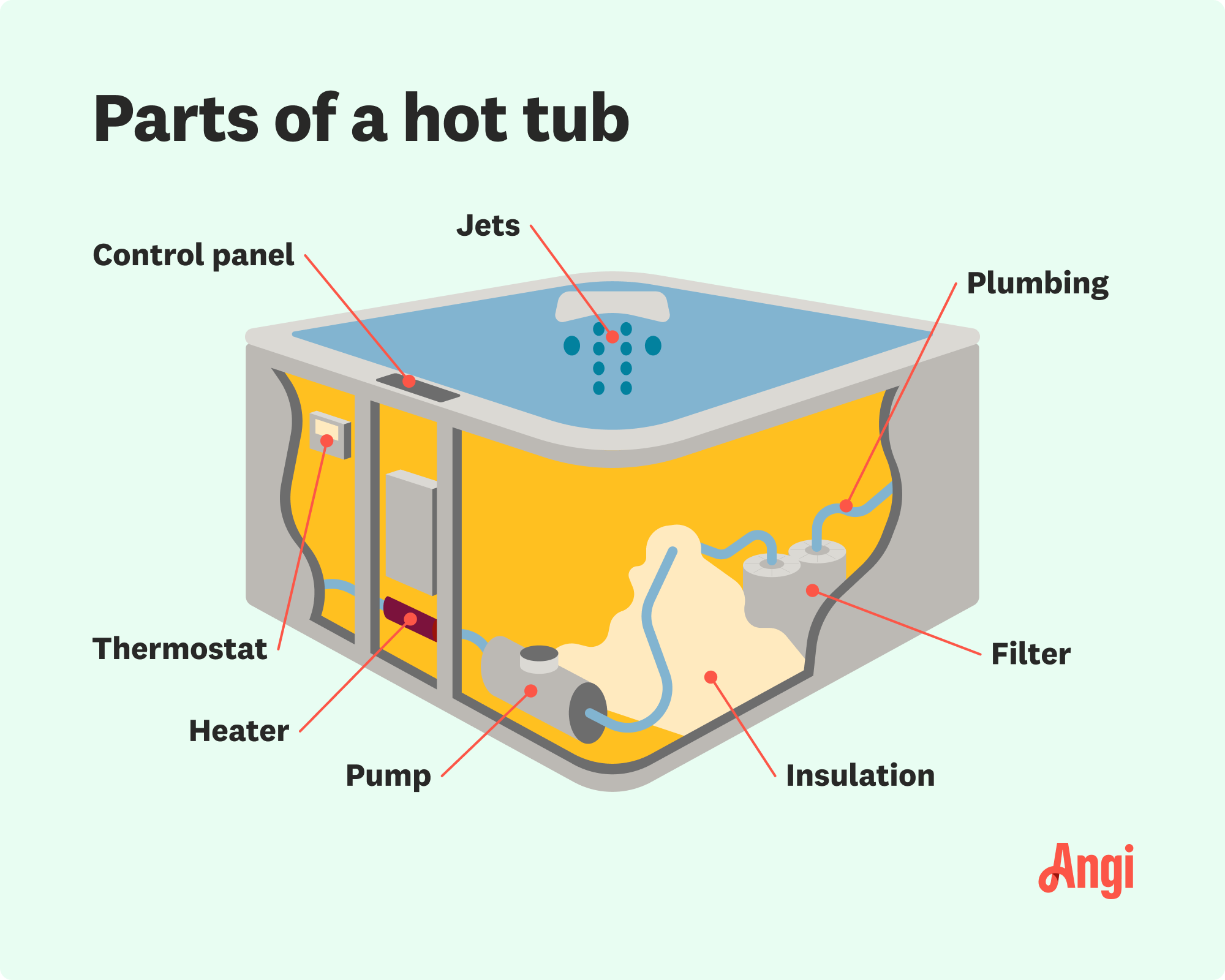
An electrical resistance heater, or heating element, is a coil or wire composed of a material called nichrome. This material boasts high electrical resistance, so it becomes hot when you run electricity through it.
Water travels through a tube that surrounds the electrical resistance heater. An electrical current raises the temperature of the heating element, which heats the water passing over it to the desired temperature through conduction. From there, a circulation pump pushes the heated water into the tub through a series of jets, giving you a relaxing soak.
The thermostat regulates the heat by controlling how hot the heating element gets and monitoring the water temperature. Once the temperature reaches a set point, the thermostat can automatically shut off power to the heating element. When the water temperature drops below that set point, the thermostat reactivates the heating element to keep the hot tub hot.
When you are using a hot tub, the control panel allows you to set the desired temperature for the water. It communicates with the thermostat to maintain the heat within the water. Depending on the model of your hot tub, you may also be able to set a timer for the jets, the pumps, and the thermostat.
Traditionally, hot tubs use electricity to conduct heat. While electrical heaters are the most commonly used heaters, there are other options available.
Gas-powered heaters require a direct hookup to a gas line, so they are typically used with in-ground spas. Similar to a gas stove, a burner ignites the gas into a flame. That flame heats a series of metal tubes or plates known as the heat exchanger. Water passes through the exchanger where it absorbs heat and gets pumped into the tub.
The thermostat in a gas-powered heater functions similarly to the one in an electrical heater. It monitors the temperature of the water, constantly adjusting the gas valve. Once the water reaches the desired temperature, the thermostat shuts the gas valve entirely.
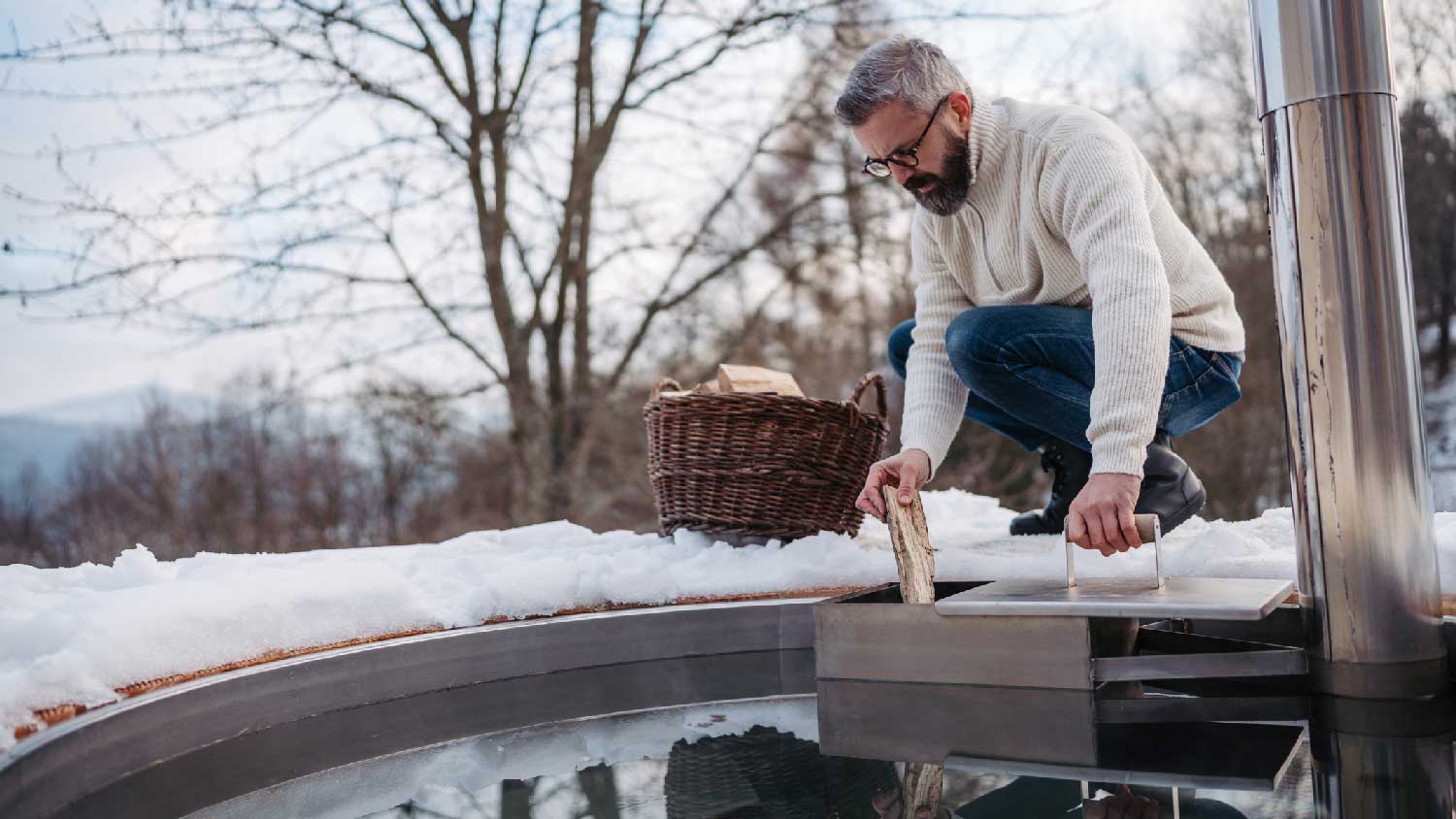

A wood-fired hot tub uses a stove attached to the tub to heat the water. There are two kinds of wood-burning heaters—submerged and external.
A submerged heater is a stove composed of marine-grade aluminum, allowing it to sit in the hot tub water. A small fence separates you from it, keeping you safe from the hot metal. You can burn logs in a chamber outside the tub, building heat within the entire apparatus that warms the water through convection.
An external stove sits entirely outside of the hot tub and is connected by two hoses or pipes. You burn logs in a chamber, and a pump circulates water through the pipes or hoses. This pump pushes the heated water from the hot chamber into your tub while circulating cooler water into the chamber to warm up.
For healthy adults, the ideal safe temperature for a hot tub is between 93 and 100 degrees Fahrenheit, though most modern hot tubs can reach a maximum temperature of 104 degrees Fahrenheit. The temperature of the water and the time spent in a hot tub should always be monitored to prevent hyperthermia and other complications.
Pregnant women, seniors, and those with health conditions should consult with a doctor before using a hot tub. Children under the age of five should never spend any length of time in a hot tub, even at its lowest setting.
Most hot tubs take an average of four to eight hours to heat up to 100 degrees Fahrenheit. The length of the heating process for a hot tub depends on several factors:
Tub size
Starting temperature of the water
Ambient temperature around the hot tub
You can get a hot tub to heat up faster if you keep the lid on the tub while it is heating. This prevents excess heat from escaping. You can also turn the jets on once they are submerged. Doing so will circulate the water, dispersing heat more efficiently.
If you find that it takes your hot tub far longer to heat up than usual, and if you detect no other hot tub problems, you may have to look at your heater.
If you ever get into your hot tub expecting a piping hot soak, but instead find lukewarm or even cold water, your heater may be the culprit. Hot tub heater replacement is an option, though many parts of the heater can undergo maintenance. A mechanical failure is not the only reason to replace a hot tub heater, however. As technology progresses, hot tub heaters become faster and more energy efficient. Upgrading your hot tub heater is a worthy, and sometimes necessary, investment.
As convenient as a hot tub can be, there are a myriad of things that could potentially prevent its heater from functioning. You can resolve some of these issues on your own if you are handy; however, you should always consult a local hot tub repair professional if you require assistance with your hot tub heater.
From average costs to expert advice, get all the answers you need to get your job done.

Discover the average hot tub maintenance cost, what impacts pricing, and how to save money. Get expert tips to keep your hot tub running smoothly all year.

We could all use some relaxation, but we don’t always have the budget. This guide will show you how much an in-ground hot tub costs—no matter the build.

Hot tub repair costs will depend on the type and severity of the issue. Our cost guide will help you decide whether to DIY or hire a professional.

Find out the average pool pump repair cost, key price factors, and ways to save. Get expert tips to budget for your pool pump repair.

Knowing how to fix a crack in a hot tub can save you a lot of money and lengthen the life of your hot tub. Here is what to expect.

Discover how much a pool vacuum costs, including average prices, installation, and maintenance factors to help you budget for a cleaner pool.