
What you’ll pay in Columbus, OH, for furnace repairs depends on many factors. Here’s a breakdown of what can go wrong and the cost to fix those issues.
Arm yourself with heat pump knowledge and stay warm and cozy this winter


Heat pump operation begins with your home’s thermostat, which sometimes needs to be recalibrated.
A heat pump works by pulling warmth from outside in heating mode or expelling heat in cooling mode.
Many heat pump issues stem from a lack of cleaning or preventative maintenance.
Heat pump issues are best addressed by the pros to ensure proper solutions and prevent further damage to your heat pump system.
When it’s chilly outside, a heat pump not blowing hot air can be frustrating and uncomfortable. To be prepared for heat pump troubleshooting, you need to arm yourself with knowledge about potential culprits. Let’s talk about the basics of heat pumps, their components, and the common issues that could be causing the lack of warm air circulation.
Whether you’re adding a heat pump to an existing or brand-new home, it’s best to hire a professional heat pump installer for this task. A pro will have the right tools, skills, and experience to ensure this essential appliance is set up accurately and efficiently.
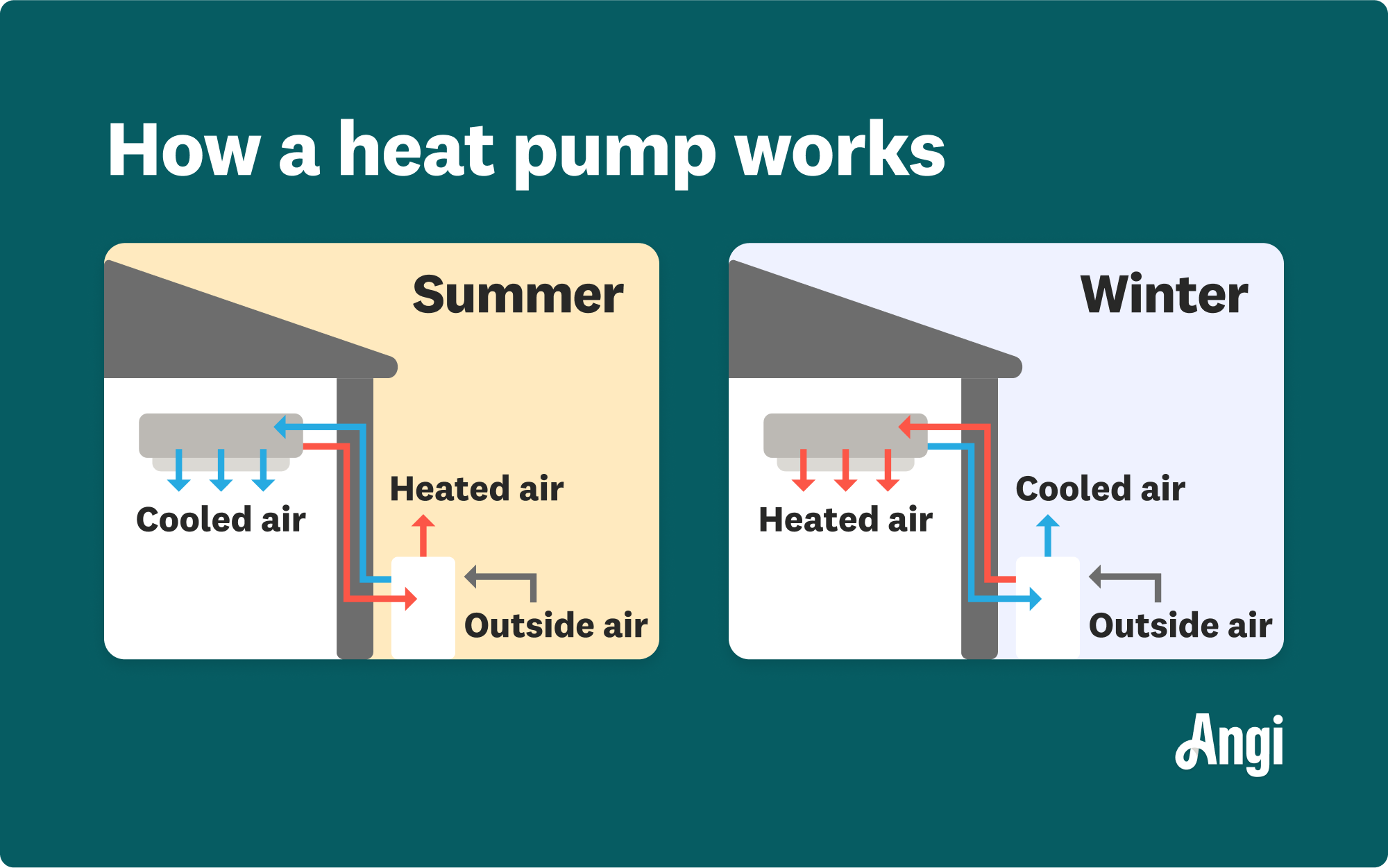
A heat pump is a versatile HVAC system that moves heat from one place to another, offering both heating and cooling functionalities. It operates on the principle of thermodynamics, using a refrigerant to transfer heat. In heating mode, the pump extracts warmth from the outside air, ground, or water and transfers it indoors. In cooling mode, the process reverses, expelling indoor heat.
Heat pumps efficiently regulate indoor temperatures, consuming less energy than traditional heating or cooling methods. This eco-friendly technology has gained popularity for its ability to provide consistent comfort while minimizing environmental impact.
Before you begin troubleshooting, it’s helpful to know some of the basic and most important parts of your heat pump.
Evaporator coil: Absorbs heat from indoor air, cooling it
Compressor: Transforms gas from evaporator coil into high-temp gas
Condenser coil: Transforms gas back into a high-pressure liquid
Expansion valve: Expands high-pressure liquid rapidly, causing it to cool
Refrigerant: Chemical that facilitates heat exchange and keeps your home comfortable
Air handler or blower: Pushes conditioned air through the ductwork
Outdoor unit: Houses the condenser coil and compressor, releasing collected heat
Reversing valve: Allows a switch between heating and cooling modes
Thermostat: Senses indoor temperature and tells the heat pump when to start or stop
Auxiliary heat strips: Provide an extra boost of warmth when the heat pump needs help
Wondering how your heat pump issue stacks up against others? According to Angi data, nearly 30% of respondents reported insufficient heating or cooling with their heat pump, making it the most common problem. Other frequent issues include not working at all, noisy or running constantly, or a frozen unit.

Low refrigerant levels can significantly hamper your heat pump's ability to produce warm air. Refrigerant is the lifeblood of the system, responsible for absorbing and releasing heat. If there's a leak or insufficient refrigerant, your heat pump's efficiency will be compromised, leading to cold air blowing from the vents.
A dirty or clogged air filter can obstruct proper airflow, causing your heat pump to struggle in heating your home effectively. Regularly cleaning or replacing the air filter is a simple yet crucial preventative maintenance task to ensure your heat pump functions optimally.
Both the evaporator and condenser coils play integral roles in heat exchange. If these coils are covered in dirt and grime, their ability to transfer heat efficiently diminishes. Cleaning these coils as part of routine maintenance can go a long way in keeping your heat pump's performance top-notch.

The outside unit of your heat pump can suffer from issues like dirt buildup, obstructions, or mechanical faults. Since this unit releases heat extracted from your home, any hindrance can result in a lack of warm airflow. Regular inspections and cleaning can help mitigate these common heat pump problems.
An inaccurate thermostat can lead to temperature discrepancies in your home. If your thermostat isn't correctly sensing the indoor temperature, it might not signal the heat pump to kick in when needed. Calibrating or replacing the thermostat could be the solution here.
The reversing valve is responsible for reversing the refrigerant flow, enabling your heat pump to switch between cooling and heating modes. A malfunctioning valve can cause your heat pump to get stuck in one mode, leading to cold air blowing when you're expecting warmth.
Auxiliary heat strips are supplementary electric heating elements that assist the heat pump in extreme cold conditions. If these strips are faulty, your heat pump might struggle to maintain warm airflow during frigid weather.
The best way to ensure your heat pump doesn’t experience regular air issues is to perform routine maintenance like cleaning and replacing its filters. You should also keep the area around the heat pump free of objects or debris and look for any leaks or disconnections. You can also hire a heat pump professional to conduct an inspection at least once, if not twice a year to make sure any potential issues are addressed before damage occurs.
While some of these issues might have simple DIY solutions, like replacing your air filter, it's often best to hire a local heat pump repair company to diagnose and address heat pump problems. These HVAC experts have the knowledge, experience, and tools to accurately identify the root cause of the issue and implement effective solutions, ensuring your comfort and the longevity of your heat pump.
From average costs to expert advice, get all the answers you need to get your job done.

What you’ll pay in Columbus, OH, for furnace repairs depends on many factors. Here’s a breakdown of what can go wrong and the cost to fix those issues.

The cost of a new AC unit depends on the size and type. Our guide breaks down AC replacement cost factors so you can decide which option matches your budget.

Regularly replacing your HVAC filter regularly is vital for a healthy system. Learn how much an HVAC filter replacement costs with this informative guide.

Explore the most common HVAC duct types, from flexible to sheet metal to fiberglass, and learn about their pros and cons.

There are few things more important to homeowners than keeping their AC systems running. Use this guide on AC leak repair to keep your home cool and comfy.

Do you have a clogged AC drain line? We dig into the reasons behind those pesky blockages and how to clear them for optimal AC performance.