
Discover storm damage repair costs, key price factors, and ways to save. Get transparent estimates to plan your home repairs with confidence.
There’s no room at the inn for Serpula lacrymans


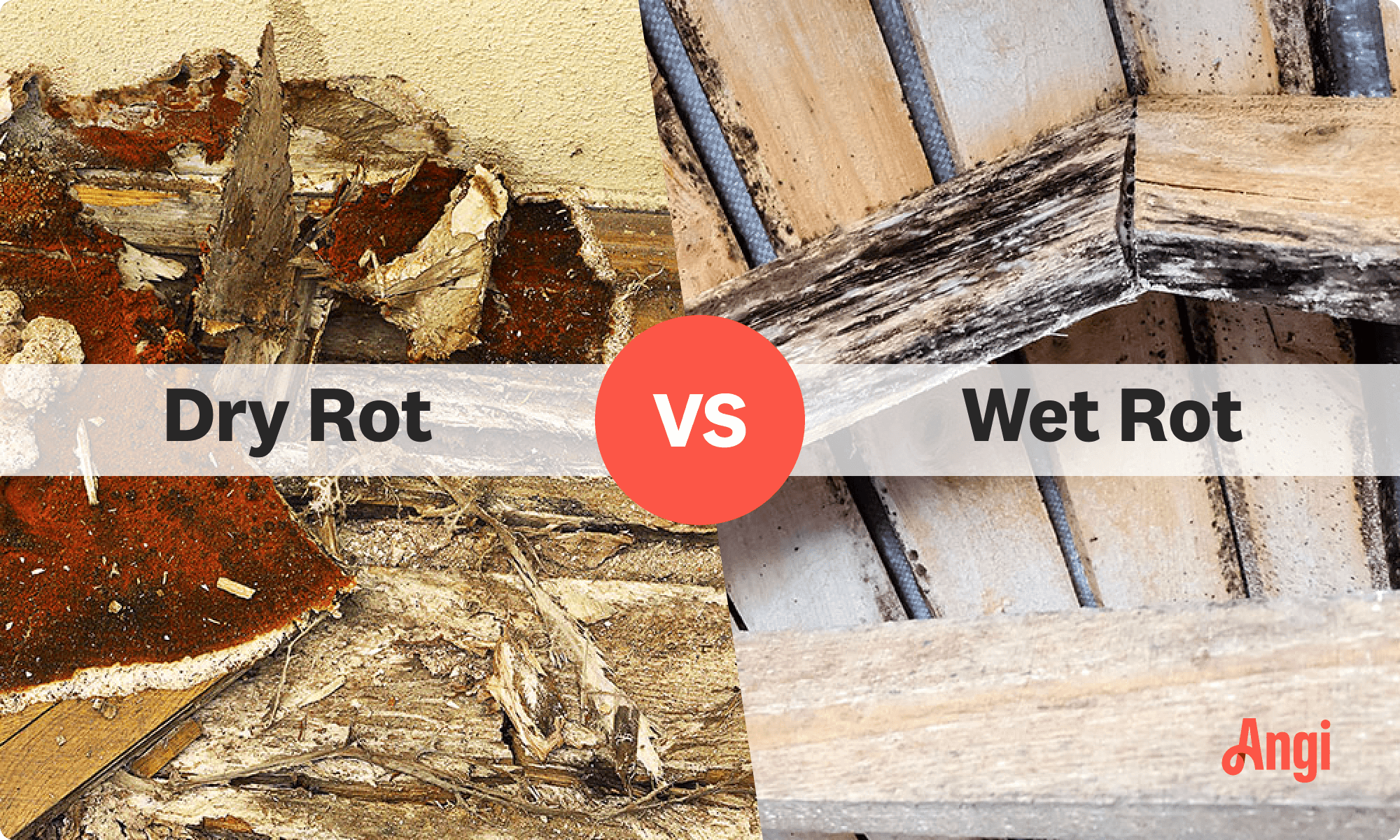
Dry rot is a form of decay in which fungi attack wood and destroy cellulose, leaving it weak and brittle.
Dry rot needs a moist environment with temperatures between 71 and 79 degrees Fahrenheit.
Proper ventilation and regular inspection are crucial in preventing dry rot.
Spotting dry rot early on can help you save your home from disaster.
What is dry rot, exactly? Your wood home is probably one of your greatest investments, so you want to keep it safe. That’s why it’s so important to spot problems, especially ones unique to your home’s structure before they turn into costly damage. Dry rot affects wood and can rot floor and ceiling beams, leading to structural problems, including deteriorated support posts and beams.
Find out if dry rot has affected your home, how to prevent it, and what to do if you discover it.
Dry rot (aka brown rot) is wood decay caused by microscopic fungi that feed on wood and consume the cell walls, which give timber its strength. Dry rot leaves dry and brittle wood in its wake and can ruin any wooden structures inside or outside your home.
Unfortunately, most people cannot identify the signs of dry rot infestation themselves. But if you don’t identify and treat dry rot immediately, it may be necessary to replace all affected timber.
Though the terms are used interchangeably, wood rot and dry rot have different meanings. Wood rot is a broad term that describes various types of fungal decay in wood, while dry rot is a specific type of wood rot caused by the fungus Serpula lacrymans. Dry rot can thrive at a low moisture level and spread rapidly across plaster and even masonry to infect new areas of wood.
Despite the name, dry rot needs moisture to start. However, it can spread without any source of moisture because it can generate moisture through the digestion of timber.
Dry rot can happen because the wood wasn’t properly dried before being used or when the wood sits in excess humidity and warm temperatures between 71 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit.
This organism targets cellulose in the wood’s structure and destroys it. The wood later shrinks and turns deep brown. Once rot starts growing, it spreads rapidly.
Dry rot can travel through various materials, including masonry, and spread throughout a property. If not stopped, dry rot will weaken the whole building to the point of decay.
Look at the areas of your home where there are humidity or water sources.
Around gutters or downspouts
Where water runs off the roof along the wall
On wooden door frames and windowsills
Near any connections between vertical and horizontal surfaces (i.e., corners)
On areas with water leaks, such as the roof
On structural points where wood meets the ground
By leaky pipes, unventilated attic space, and damp basements or crawl spaces
Several signs indicate the presence of wood rot. If you see any of these signs, you probably have dry rot.
Visible fungal growth that looks like a fluffy white cobweb
Strained drywall
Water droplets on the surface of the wood
Brown dark timber
Brittle or weak wood
A musty or damp smell
Patches of light purple, orange, or brown that peels easily
Grayish strands on the wood or timber
Fruiting mushroom bodies among the spores
Test the area by poking it with a screwdriver. If it penetrates the wood or makes the wood flake easily, there is likely rot. Contact a local home inspector so they can look into this further and check your home for signs of wood rot.
While dry rot spores are not harmful themselves, a house with dry rot isn't a pleasant place to live in, especially with the smell of damp soil filling the air. The damp conditions pose a health hazard for infants, older people, and those with respiratory diseases.
Beyond this, dry rot is very dangerous to your home itself, as it can quickly cause extensive structural damage.
Dry rot, driven by the fungus Serpula lacrymans, has the power to wreak havoc on your home. Left untreated, it can cause damage to your entire property, as it spreads quickly to any moist wood and even porous masonry. Once present on the wood, it will deteriorate it, impacting the structural integrity of your house.
In addition, the moisture in your home that allows the dry rot to thrive can cause respiratory problems (especially for those with asthma). A small number of people may find themselves allergic to the fungus that causes dry rot.
The deterioration, and subsequent damage, is progressive and can snowball quickly, so the longer you wait to treat dry rot, the further it will spread and the worse the situation will be. When you have a toothache, it’s best to go to the dentist sooner rather than later to prevent a small problem from becoming a large one. The same rule applies to dry rot.
Once you identify that dry rot has started, you’ll need to stop it immediately. First, find the source of the problem and eliminate it. A fungicide with borate is one of the most effective ways to kill fungus and prevent dry rot. However, this solution will only work if the dry rot is at the first stages. For more advanced cases, you will need to replace the affected wood with treated timber.
Because dry rot can move so quickly and cause such damage, you’ll want to get a water damage restoration pro or a local carpenter to evaluate how to treat the dry rot properly. You can also call a local handyperson if they have experience with dry rot.
When it comes to dry rot, prevention is the key. It’s easier and more cost-effective to prevent decay rather than fix it. The key is to limit wood exposure to moisture in your home with these tips:
Seal all cracks with caulk. Be sure to scrape away old hardened caulk and replace it with fresh caulk.
Clean gutters regularly—at least twice a year—to prevent blockages that can lead to water running over the side of your home.
Make sure to prime any outdoor wood on all sides before painting.
Check for plumbing leaks and repair any problems ASAP.
Add a canopy over the entryway to keep the rain away from the doors.
Use a good dehumidifier in the basement or any house room subject to high humidity.
Make sure to ventilate bathrooms, attics, crawl spaces, and kitchens properly.
Repaint exterior windows and siding if the paint is cracked or peeled.
Sweep standing water from outdoor decking as soon as the rain stops.
Check all flashing to ensure water can’t get inside your home.
Have your house inspected annually to identify any cracks or potential damage.
Always use decay-resistant or pressure-treated wood for exterior projects.
Be proactive and on top of any small issues on the roof and repair them ASAP.

From average costs to expert advice, get all the answers you need to get your job done.

Discover storm damage repair costs, key price factors, and ways to save. Get transparent estimates to plan your home repairs with confidence.

When your home project requires a professional at the helm, how much are construction management fees, and how do they determine their rate? Let's break it down.

Recessed living rooms used to be popular but have fallen out of favor. This guide discusses the cost to raise a sunken living room to modernize your home.

When planning a home renovation or remodel, asking your contractor to reduce the price of the job is never an easy task. But negotiation is possible! Read these tips for negotiating with a contractor the right (and effective) way.

Discover the average home elevator maintenance cost, key price factors, and expert tips to help you budget for safe, reliable elevator upkeep in your home.

If you’re replacing your roof or flooring, you might be wondering, “How much plywood do I need?” The answer comes through a simple calculation.