
The cost to install a C-wire ranges based on materials and labor, but it only takes an hour or two. Here’s a guide on the project costs to expect.
Shedding light on the better electrical option for your home


Circuit breakers use a switch mechanism that trips when overloaded, while fuse boxes contain a single wire that melts when overloaded.
Circuit breakers are reusable and are often found in newer homes, while fuse boxes are single-use and more common in older homes.
Circuit breakers are more expensive to install, but they cost less to repair or replace than fuse boxes.
Although they serve the same overall purpose, fuse boxes and circuit breakers work in different ways to protect your home’s electrical system. Usually found in older homes, fuse boxes rely on fuses that melt and break the circuit when overloaded, requiring more frequent replacement.
Circuit breakers, which are standard in modern homes, use a switch mechanism that trips during a fault and can be easily reset without needing new parts. Let’s dive into the differences between circuit breakers and fuse boxes so you can decide which makes the most sense for your home.
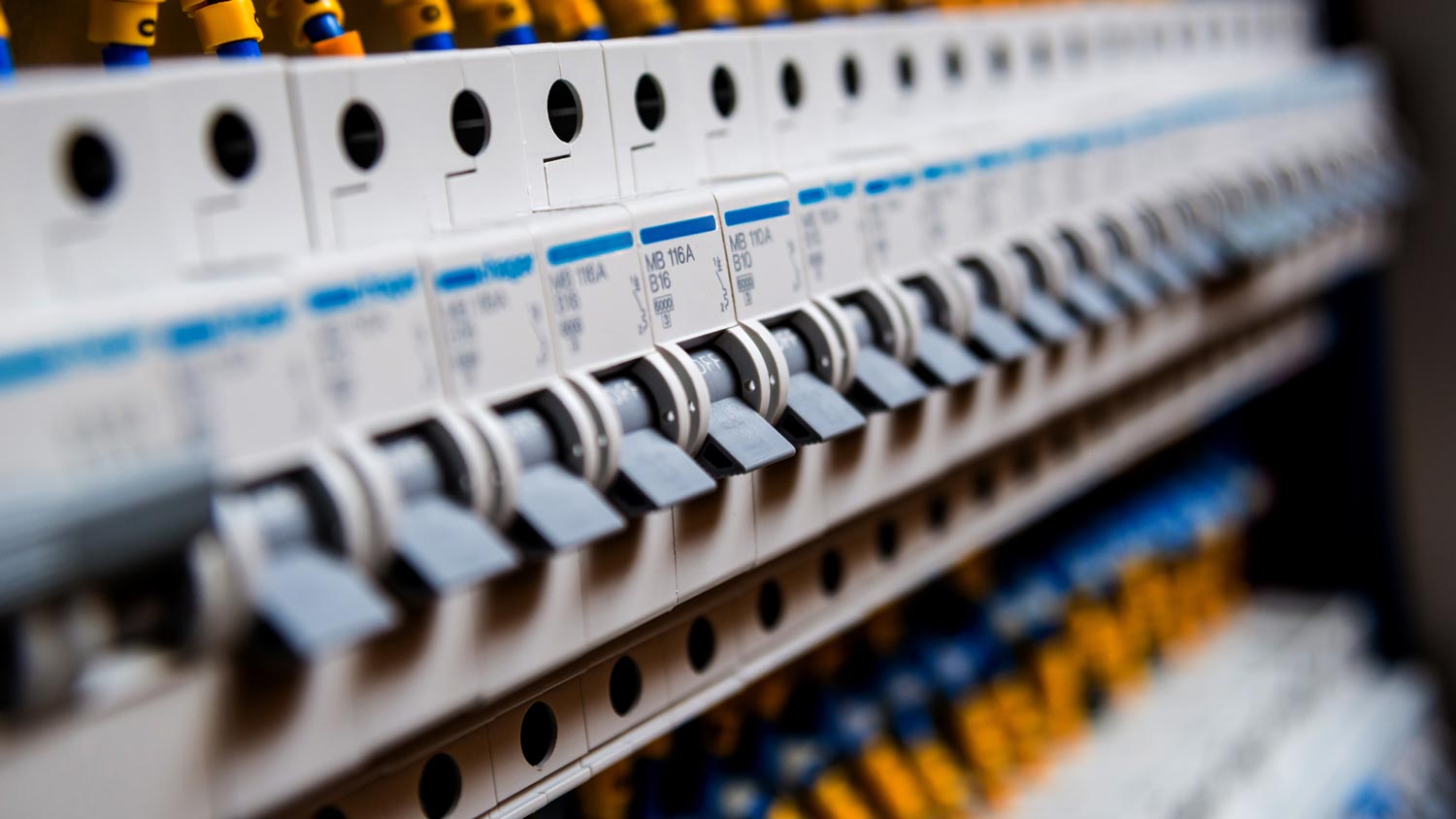


While both circuit breakers and fuse boxes are arguably the most essential components in your home, they differ when it comes to visuals and execution.
| Type of Difference | Circuit Breakers | Fuses |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Can be reset | Must be replaced |
| Characteristics | Trip on overload | Blow when overloaded |
| Maintenance and Durability | Reusable | One-time use |
| Convenience and Usability | Easy to troubleshoot | Simpler design |
| Era of Use | Used in modern homes | Used in older homes |
Both circuit breakers and fuse boxes are part of your home’s electrical panel, and they are in a metal service box that accepts power from your utility company. Circuit breakers have rows of small, rectangular switches, and fuse boxes have either glass or ceramic plugs and exposed wiring.
Circuit breakers are available in standard, GFCI, and AFCI (Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupter). They also offer single or dual-functionality and different amp capacities depending on your home’s electrical usage.
Fuse boxes typically contain six to 12 fuses and are available in screw-in (plugs) or cartridges for larger appliances. Fuse boxes come in 60-amp capacity and offer less power than circuit breakers.
Circuit breakers are safe and reliable and protect your home from overheating, fires, and short circuits. You can use your circuit breaker until the end of its lifespan or when it requires replacement—usually decades later. However, frequent trips and overloads can wear out the breaker, and they require more comprehensive equipment to operate.
Fuse boxes offer more reliability because it’s easy to switch out blown fuses. But they also age and degrade over time, and you’ll eventually have to replace the unit when it fails or as you require more amperage.
Circuit breakers are typically more expensive to purchase and install than fuse boxes. The average cost to replace a circuit breaker box is $1,150.
Fuse boxes are less costly to buy and replace blown bulbs. The cost to replace a fuse box will run between $200 to $2,000.
An electrical pro should install both circuit breakers and fuse boxes. Due to wiring, code, permit requirements, and the risk of electrocution, you should hire an electrical professional near you for installation and service.
Remember, fuse boxes are older technology. Ask your electrician if they have experience with this project before beginning.
You can reset your circuit breaker yourself by locating the tripped switch and turning it from OFF to ON. If the problem persists or you can’t flip the switch yourself, it’s best to call an electrical pro.
When you blow a fuse, you can find replacement fuses available for a low price at any hardware store. There are different types available depending on voltage levels. You can also replace a blown fuse by yourself—you’ll want to ensure the new fuse has the correct amperage capacity. When you blow a fuse, you’ll need to replace it before resetting your entire electrical panel. However, using incorrect voltage bulbs in the box increases the risk of electrical overload and fires. Fuse boxes houses exposed wiring, which could pose a danger to inexperienced homeowners. Some insurance companies will not cover homes with fuse boxes due to increased fire risk.
You should inspect your circuit breaker every one to three years and perform a routine trip test every three to five years to ensure that all breaker switches are in working order. You can expect to pay $40 to $50 per hour to hire an electrician for maintenance.
Fuse boxes require less maintenance, but you’ll always have to replace a blown fuse before turning on your electrical panel. You can expect to pay between $5 to $10 for a multi-pack of replacement plugs.
Circuit breakers typically last between 30 to 40 years, while fuse boxes can last about 50 years. At this point, both circuit breakers and fuse boxes will require electrical updating and new, modern equipment.
Circuit breakers are used in post-1960 homes, and homeowners can restore power with a simple flip of a switch. They provide a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) outlet, which prevents electrical shock. Homeowners can shut off electricity to labeled individual circuits rather than the entire home. The breaker box hides electrical components, making it safe for inexperienced homeowners. Fuse boxes offer 60-amp power, while circuit breakers provide 100 to 200+ amp power.
If your home still uses an older fuse box, it might not provide enough power for a modern home. (Your home may have other outdated electrical elements, too.) If you’re regularly experiencing blown fuses, you might consider upgrading to a circuit breaker box that can handle your higher amperage needs.
Wonderful personality, works hard, constant communication.
We went over what was to be done and he followed to the letter except where he found bunny nest. Good call! Cheerful, easy to work with
Bruce and Nate were exceptional!! They tiled our basement shower and it looks amazing!!! They made the design look outstanding - so visually pleasing. Bruce also guided us in what kind of grout would go well with the tile and pebble flooring we picked out - he's the expert! He also put in 3...
They were good will use them agian thank you.
From average costs to expert advice, get all the answers you need to get your job done.

The cost to install a C-wire ranges based on materials and labor, but it only takes an hour or two. Here’s a guide on the project costs to expect.

Rewiring a house can be a complex project but don’t let it catch you off guard. Read this to plan ahead and discover the cost to rewire a house.

Whether you’re shopping for a new home or simply doing a safety check on your current place, learn what factors influence an electrical inspection cost.

Today’s polarized plugs and outlets have a hot and neutral side, which is important for any receptacle wiring. Here’s what that means, why it happened, and how to take advantage of it.

Wondering who to call for a fast and easy lamppost installation? Our guide covers who should install a lamppost and the general cost for this project.

Learn how to install a C-wire as part of your smart thermostat installation and discover other options that may work for your HVAC wiring.