
Moving a furnace a few feet is not a huge matter. However, moving a furnace to another room or different part of the house will probably cost a few thousand dollars. It's a major job involving numerous different professionals.
Choose the best system to keep warm on chilly nights


Baseboard heaters cost less to install, but are more expensive to run than forced air.
Forced air heats your home faster than baseboard heaters, which only serve one room at a time.
Baseboard heaters don’t require ductwork, while forced air relies on it.
Deciding whether to install baseboard heating or forced air in your home? Choosing a heating system is an important task, and you want to pick the option that will keep you warm on frigid winter days.
There are many types of heating systems to choose from, but the two of the most common are baseboard heating and forced air. This guide will compare baseboard heating vs. forced air to show you the key differences, pros and cons, and how to pick the right system for your home.

There are some significant differences between baseboard heating and forced air to consider when picking which is right for your home. One main difference is that baseboard heating does not require ductwork like forced air, which makes it easier to install.
Baseboard heating also allows you to control the temperature in each individual room, whereas forced-air utilizes a thermostat for the entire residence. However, forced air can heat your home faster than baseboard heating, plus it heats the entire home evenly.
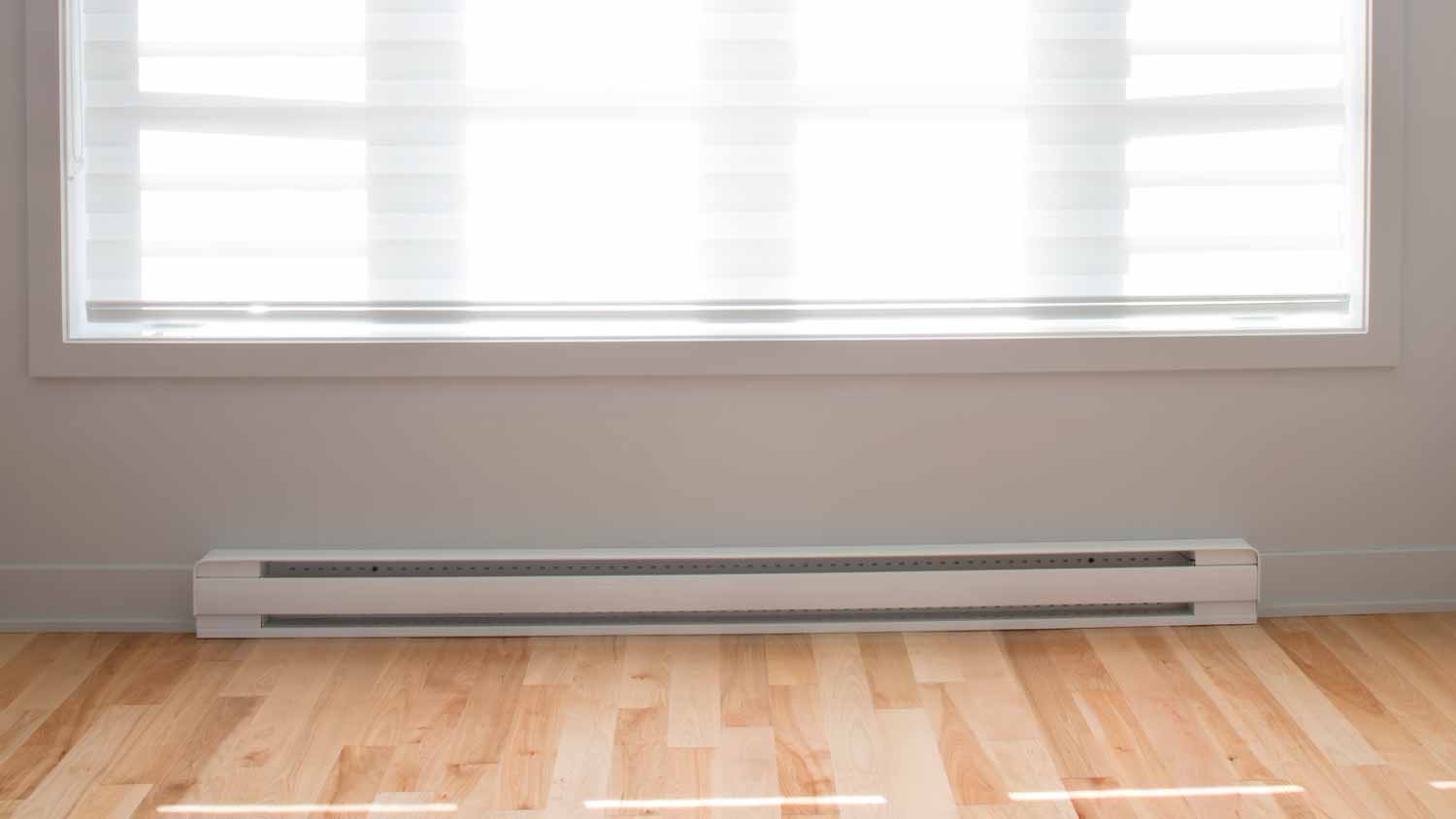

Baseboard heating is a type of heating system that does not require furnaces, vents, or ductwork. The baseboard units are installed along the base of walls and can run on gas, electric, or hydronic power. Electric units utilize heating elements to warm the air, while hydronic units use heated water to provide warmth. This system creates a convection current that circulates the warm air and provides consistent heating in the home.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Zoning capabilities for each room | Takes up floor space |
| Can be energy efficient | Hot unit is a fire hazard |
| No ductwork required | Leads to higher utility bills |
Best For:
People who want to control the temperature of each room individually
Homeowners looking for a heating system that doesn’t require ductwork
Smaller homes or home additions
One of the best things about baseboard heating is that you can control the temperature of each room, known as zone heating. So, if you have a guest room that isn’t frequently used, you can close the door and lower the thermostat to save on heat costs. This heating system is also technically energy efficient because it converts all the incoming energy to heat.
Another perk of baseboard heating is that it doesn’t require ductwork to heat your home. This is a major benefit to homeowners with small homes or home additions who are searching for a less costly heating system to warm their space.
While baseboard heating has its benefits, there are some drawbacks to consider before ruling out other types of systems. One major con is that it takes up floor space in your home. Additionally, due to the risk of fire from an overheated baseboard heater, you cannot put objects, materials, or furniture in front of it. While that eliminates the fire hazard, it limits the space around the heat system.
Electric units can be hot to the touch and even cause burns to the skin. Another downfall is that they don’t circulate heat as well because most models do not have blowers to distribute the heat. Electric baseboard heaters can use more electricity than other types of heating systems, which can increase utility bills. If you heat your home for ten hours a day, running a baseboard heater could cost between $500 to $1,000 per month, depending on home size and insulation quality.
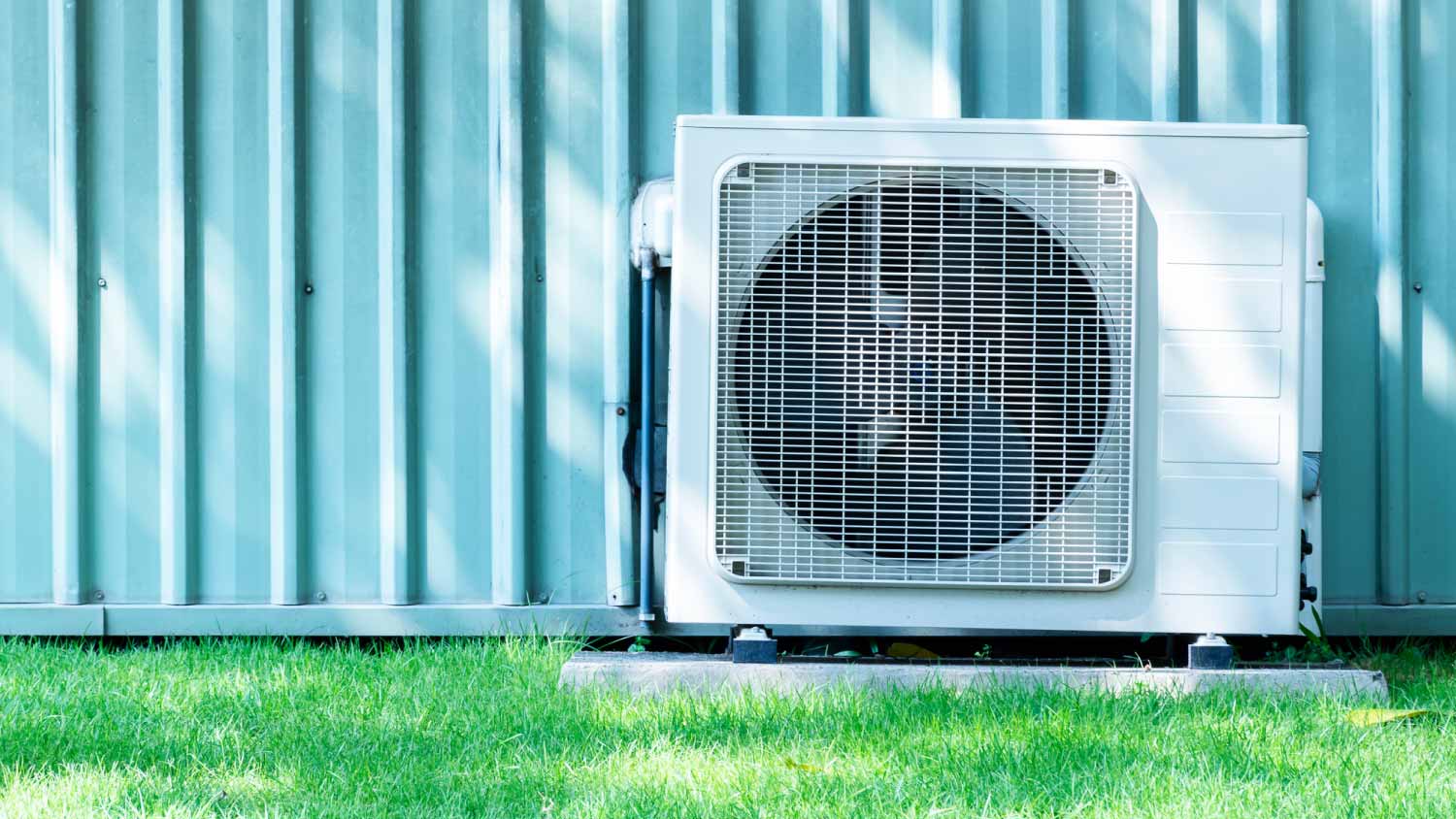
Forced air heating can be gas or electric. It uses a heat exchanger and blower fan to distribute heat throughout ductwork and release it through vents into the home. The system can have a furnace or a heat pump, and it’s controlled by a thermostat to keep the residence at a comfortable temperature. Forced air efficiently regulates consistent temperatures throughout the entire house or building.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Heats home quickly | Costly to install |
| Easy to operate | Potential health issues if not maintained |
| Improves air quality | Ductwork can leak |
Best For:
Homeowners looking for an efficient system that heats their homes quickly
Homes with existing ductwork
Larger homes and buildings
The biggest benefit of investing in forced air heating is that it heats your home faster than baseboard heating. It heats and distributes the air quicker because baseboard heaters rely on convection heating, while forced-air utilizes blowers.
This system is easy to operate after installation, and you can control the temperature of the entire home with a thermostat. Since forced air has an air filter, it can improve air quality by removing dander, dust, and other allergens that are circulating in your house.
Sure, there are quite a few pros to forced air, but the cons may change your mind about whether this is best for your budget and home. The price of a forced air system depends on many factors, but a new furnace costs between $2,825 and $6,880. That price may not include ductwork, which you will need to install if your home doesn’t have it.
Although any type of heating system needs to be maintained, forced air can cause health issues if it’s not cleaned correctly. Mold and dust can accumulate in the ducts and should be professionally cleaned at least every three to five years. Ductwork can also have leaks which can decrease heating efficiency and lead to uneven heating.
Now that you know the difference between baseboard heating and forced air, let’s compare them further to see which is best for your home.
Although baseboard heating offers different options, such as electric and hydronic units, forced air has more customizations and options available. For example, some systems have programmable thermostats that also offer zone heating, and you can add air purifiers and humidifiers to them.
The lifespan of either system depends on several factors, such as whether it’s installed correctly, home’s climate, amount of use, and amount of maintenance. However, the average lifespan for forced air and baseboard can range between 15 to 20 years or more if properly maintained. That’s why it’s essential to keep units clean and professionally maintained throughout its lifespan.
When it comes to installing a heating system on a budget, baseboard heating wins for lowest upfront cost. The average cost to install electric baseboard heaters ranges between $400 and $1,510, whereas a furnace or HVAC system can cost $2,500 on the low end. But keep in mind that the monthly cost to run baseboard heaters is much higher than the average monthly utility bill for forced air heating.
Even though you should hire a baseboard installation company near you to safely install your new heaters, they are still much easier to add than forced air. Baseboard heating doesn’t require running any ductwork; it only needs to be mounted on the wall and hardwired into your electrical system. This ease makes installation simpler and faster than forced air units.
From average costs to expert advice, get all the answers you need to get your job done.

Moving a furnace a few feet is not a huge matter. However, moving a furnace to another room or different part of the house will probably cost a few thousand dollars. It's a major job involving numerous different professionals.

Do you know what it will cost to reroute ductwork in your home? Discover the cost factors and other considerations of this HVAC project.

Whether your energy bills are out of control or you can’t keep your home comfortable, it’s good to know what costs to expect before you pay to insulate your ductwork.

Discover wood pellet cost estimates, including price per ton, bag, and key factors that impact your total heating expenses.

Leaking AC coils can compromise your entire home cooling system. Look for these six signs of a leaking evaporator coil, and schedule a repair ASAP.

A rooftop AC unit isn’t just for commercial properties—but is it the right solution for your home? This guide will show you the pros and cons.